How have the shopping malls we know adapted to changes in time and technological advancements? From their inception to the present, and looking ahead to their role in future smart cities, shopping malls have transcended being mere places of purchase to fundamentally altering our lifestyles and urban landscapes. Today, shopping malls face new challenges.
This article provides in-depth information for readers interested in the evolution of shopping malls, current shopping trends, and the changes future technologies will bring. We explore how shopping malls can position themselves as vital, inclusive, and sustainable components of future city living, from their changing roles to their sustainable functions within smart cities.
- The Changing Role of Shopping Malls: Past Versus Present
- Shopping Mall Market Response Post-COVID-19
- The Sustainable Role of Shopping Malls in Future Smart Cities
- Implications (The Role of Shopping Malls in Future Smart Cities)
The Changing Role of Shopping Malls: Past Versus Present Past Shopping Malls
Past Shopping Malls: The fundamental reason for the emergence of shopping malls was to provide a space where people living in the suburbs could easily access and shop for the latest items. This space evolved into a gathering place, subsequently offering cultural experiences similar to a comprehensive shopping center.
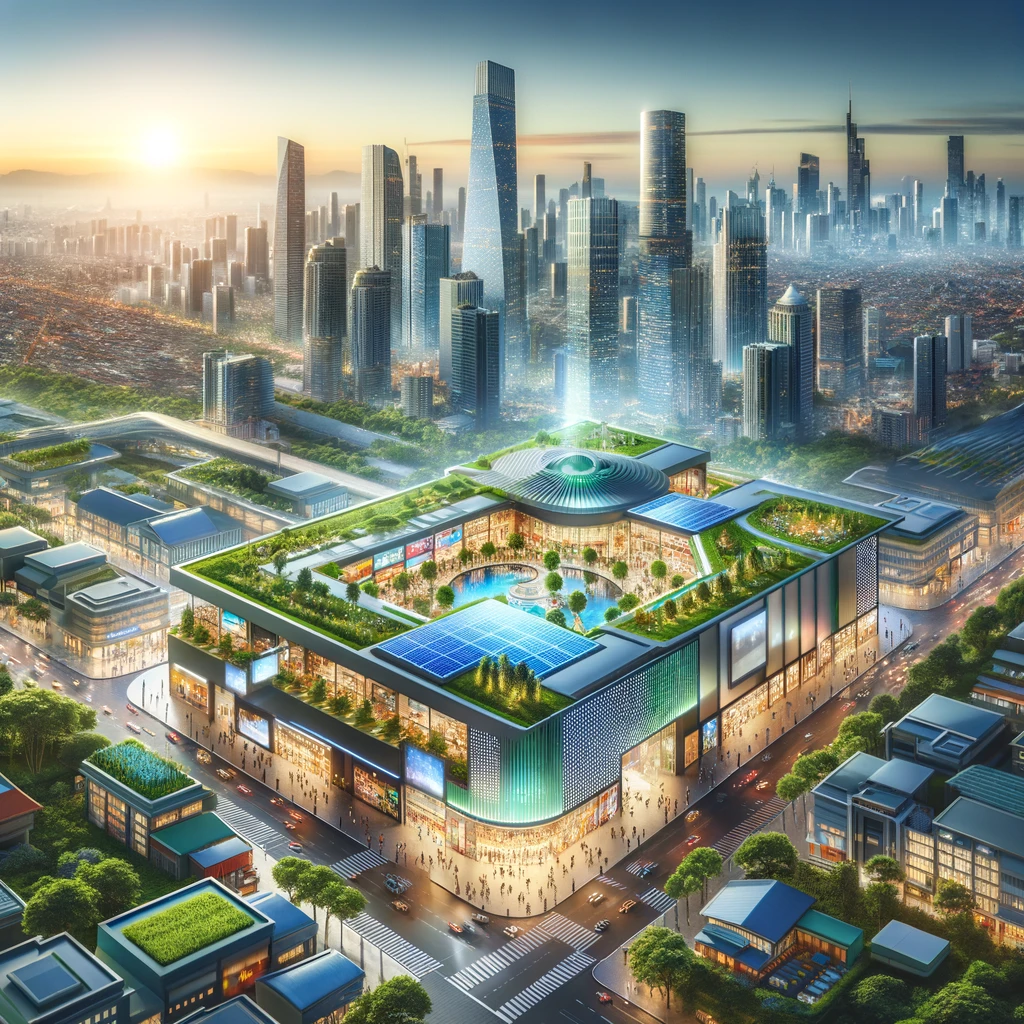
Present Shopping Malls: Today’s malls offer a blend of shopping and entertainment. They host brands that allow friends to purchase the latest products, offering a variety of apparel and goods. Entertainment options include cinemas, diverse dining venues, and events like Christmas celebrations. However, visiting malls now, you might notice they are not as crowded as before, with tourists making up most of the customer base. The shift towards online shopping and the impact of COVID-19 have reduced the need for physical malls.
According to Retail Dive, mall foot traffic initially dropped by almost 90%, with a 66.8% decrease by the end of 2020 compared to 2019. The increase in online shopping is a major factor in this decline. Overall, foot traffic in apparel stores decreased by 5% from 2019, with significant decreases in major retailers like Macy’s and Kohl’s.
Newly planned malls emphasize the importance of Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) over fashion, highlighting the significance of food, desserts, and cafes in changing the overall atmosphere of the mall.
Shopping Mall Market Response Post-COVID-19 Operators and Retailers’ Response
Globaldata indicates significant changes in mall foot traffic during the pandemic, with suburban shopping centers recovering faster than urban ones. Consumers have shown a preference for outdoor malls, leading to a lower decrease in foot traffic compared to indoor malls. Some regions saw an increase in mall visits during the summer of 2021, surpassing pre-pandemic levels.
Acceleration of Digitalization and Omnichannel Strategies: The rise in online shopping during COVID-19 has led to an acceleration in digitalization and the adoption of omnichannel strategies by many malls and retailers. Consumers expect a seamless shopping experience across online and offline platforms, a trend that will continue.
Shift to Customer Experience: Post-pandemic, consumers view shopping as an experience beyond mere purchases. Malls are enhancing customer experiences through virtual reality (VR) experiences, personalized shopping services, and an increase in entertainment and leisure activities.
Sustainability and Social Responsibility: COVID-19 has raised awareness about environmental sustainability. Malls and retailers are adopting eco-friendly operations and offering sustainable products, demonstrating social responsibility and supporting local economies.
Flexibility and Adaptability: The pandemic highlighted the importance of flexibility and adaptability for malls. To prepare for uncertain future market conditions, malls are utilizing their spaces for multiple purposes, temporary pop-up stores, and event spaces.
The Sustainable Role of Shopping Malls in Future Smart Cities
Need for Innovation Green Infrastructure and Architecture: Modern malls like Singapore’s City Square Mall are adopting green architectural elements, shifting towards sustainable design. Finland’s first 100% carbon-neutral shopping center, Lippulaiva, boasts a 3,500 square meter green roof.
Sustainable Transportation Solutions: Visitors to Mexico City’s shopping centers receive incentives for using public transport, carpooling, and eco-friendly vehicles.
Integration of Solar Energy: Shopping centers are meeting 100% of their digital signage’s power requirements through solar energy.
Malls are becoming community hubs that foster meaningful connections. By hosting sustainable living workshops, composting classes, and recycling drives, they are spreading ecological consciousness throughout the community journey.
Moreover, indoor malls must offer family-friendly (including pets) environments, while outdoor malls should effectively implement a contemporary downtown ambiance.
Malls are undergoing future-oriented changes through five key elements: customer centricity, data, efficiency, logistics, and service, striving to serve the community and become genuinely useful spaces.
Implications
Firstly, malls can no longer attract customers solely with shopping, entertainment, and food. The online activation of shopping and entertainment necessitates spaces for family, cultural experiences, new encounters, and learning. Understanding the history and current role of malls is crucial for comprehending the future of smart cities. Like new towns that offer urban living experiences, smart cities must feel familiar and natural to people, posing a challenge for all smart cities.
To build the ultimate smart city, collaboration among various companies is necessary. A correct smart city can be formed only when numerous infrastructures and technologies are integrated in a complex manner. To assist with this, SimpleCrystal will continue to create the MaterPiece series by compiling helpful materials.